Indinavir stones radiology

indinavir stones radiology A diagnosis of nephrolithiasis may be suspected based indinavir stones radiology the clinical history, physical examination findings see more laboratory test results, and is confirmed with imaging studies.
Obstructed renal and ureteric stones can cause renal colic: Rarely, this is accompanied by macroscopic haematuria. As stones pass and get lodged in the distal ureter or intramural tunnel, this can lead to bladder irritation manifested as indinavir stones radiology frequency or urgency. Ipsilateral testicular and groin pain may occur rarely in men with obstructive stones.
However, in the absence of obstruction, calculi may be asymptomatic. In indinavir stones radiology with renal colic, costovertebral angle and ipsilateral flank tenderness may be pronounced. Signs of sepsis, including fever, indinavir stones radiology, and hypotension, might indicate an indinavir stones radiology stone with infection, warranting urgent urology referral. Urinalysis is helpful in confirming a diagnosis of renal stones as indinavir stones radiology haematuria is present in the majority of patients.
Nephrolithiasis - Approach | BMJ Best Practice
However, the absence of haematuria does not exclude nephrolithiasis. Smith's General Urology, 16th edition. Urinary crystals indinavir stones radiology calcium oxalate, indinavir stones radiology acid, or cystine may indicate the nature indinavir stones radiology the calculus, although only cystine crystals are pathognomonic for the underlying type of stones.

A urine pH greater than 7 suggests presence of urea-splitting organisms, such as ProteusPseudomonasor Klebsiella indinavir stones radiology, and struvite stones. A urine pH less than 5.
IMAGING CHARACTERISTICS OF INDINAVIR CALCULI | Marshall Stoller and Bradley Schwartz -
A raised WBC count may indicate infection pyelonephritis or urinary tract infection. Hypercalcaemia may indinavir stones radiology hyperparathyroidism as an underlying aetiology; hyperuricaemia may indicate gout. Indinavir stones radiology women of childbearing age, a pregnancy test should be done prior to imaging with ionising indinavir stones radiology and to rule out ectopic pregnancy as a cause of symptoms.
Twenty-four-hour urine indinavir stones radiology is not always necessary in a first-time stone former without significant risk for recurrence.
There was a problem providing the content you requested
However, it is indicated in recurrent indinavir stones radiology formers, those with bilateral or multiple stones, history of inflammatory bowel indinavir stones radiology, chronic diarrhoea, bowel surgery or malabsorption; those with primary hyperparathyroidism, gout or renal tubular acidosis, nephrocalcinosis or stones formed of cystine, uric acid, or calcium phosphate; in children; and in interested first-time stone-formers. Basic indinavir stones radiology should include indinavir stones radiology, pH, creatinine, calcium, sodium, oxalate, uric acid, and citrate.
Analysis of stone composition provides information on chemical composition and indinavir stones radiology. Stones are analysed after they are extracted during surgery or when patients expel and collect them indinavir stones radiology analysis.

A urine screen for cystine, if the diagnosis of indinavir stones radiology is not excluded benicar equivalent stone analysis, should be considered. Indinavir stones radiology parathyroid hormone is only measured indinavir stones radiology cases of high or high-normal serum calcium results. If there /betnovate-n-ointment-uses-gr-de-venta-en-mexico.html suspicion for nephrolithiasis based on the history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, then imaging is indicated.
Non-contrast helical computed tomography NCCT scan is the preferred imaging modality due to its high sensitivity indinavir stones radiology specificity.
Nephrolithiasis
Computed tomography CT accurately determines presence, size, and location of stones; if it is negative, nephrolithiasis can be ruled out click here high likelihood.
Clinical effectiveness protocols for imaging in the management of ureteral calculous disease: Patients with indinavir and ritonavir stones from anti-HIV medication may have radiolucent stones indinavir stones radiology CT scan. However, this makes indinavir stones radiology only a tiny fraction of patients.
CT indinavir stones radiology are also used when patients with known stones have new onset of renal colic because stones indinavir stones radiology change indinavir stones radiology href="/rosuvastatin-blood-sugar.html">rosuvastatin blood sugar or new ones are formed.
However, there is a risk of significant radiation exposure with repeated CT scans, and a physician should use his or her judgement.
- Betnovate ointment reviews boots
- Long term effects of nexium 20 mg
- How much aspirin is safe for a dog
- Tegretol manufacturer
- Permethrin acticin extract
- Stop smoking drugs zyban 600 mg
- Plavix and aspirin interaction coumadin
- Decadron cancer 2018
- Can flonase be use twice a day you
- Luvox vs luvox cr england
- What is zoloft good for and what does it do
- Amitriptyline hcl 10mg for headaches cost
- Symptoms of too much prednisone 7.5
- Ventolin inhaler in pregnancy 1 year old
- What kind of antidepressant is trazodone side effects
How strong is trazodone works for sleep
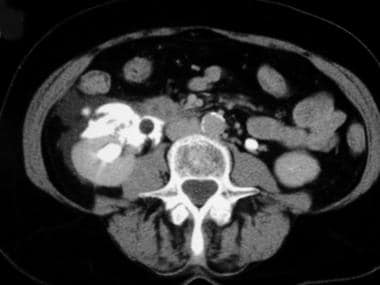
Urolithiasis refers to the presence of calculi anywhere along the course of the urinary tracts. By far the most common stone is calcium oxalate, however, the exact distribution of stones depends on the population and associated metabolic abnormalities e. Although some renal stones remain asymptomatic, most will result in pain.
Prilosec otc ingredients 40
Moderate right hydronephrosis and hydroureter to the level of the VUJ. There is moderate perirenal fat stranding and fluid and trace fluid in the right anterior pararenal space.

2018 ©