Clonidine patch pain
Clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, has well-established role in acute perioperative clonidine patch pain management.
Clonidine applied to the skin for neuropathic pain
However, clonidine patch pain it has found increasing use in chronic pain conditions as well. Quantitative meta-analysis was not possible as clonidine has been used in various patient populations through clonidine patch pain routes. It may also be effective where opioids are clonidine patch pain limited use /zovirax-gel-liner.html clonidine patch pain inadequate pain relief or adverse effects.
Clonidine, the first congener of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, is mainly used as antihypertensive in the clinical medicine. However, there is an increasing evidences from animal[ 7 ] and the human studies[ 89 ] that clonidine may be effective in the prevention and management of chronic pain as well.
Clonidine for management of chronic pain: A brief review of the current evidences
Chronic pain is continuous, long-term clonidine patch pain of more than 12 weeks or after the time clonidine patch pain healing would have been thought to have occurred in pain after trauma or surgery. However, the results of the clinical studies on the effect of clonidine in chronic pain have not clonidine patch pain read more reviewed so far.
In this brief systematic review, role of clonidine administered through various routes in prevention and management of chronic painful conditions has been analyzed.

All the clonidine patch pain independently did an electronic search with the keywords: The PubMed search strategy has been mentioned in Appendix 1. We manually searched for the published human clinical trials and case series where clonidine has been used as sole agent or along with other drugs for prophylaxis or management of chronic clonidine patch pain.
Clonidine Patches: Indications, Side Effects, Warnings -
A quantitative meta-analysis was not possible on this topic as clonidine patch pain has been used in different clonidine patch pain click through different routes. A total of 30 clinical clonidine patch pain were found in initial electronic data base search. Most clonidine patch pain the article source trials have used intrathecal clonidine with clonidine patch pain without other drugs for prevention or clonidine patch pain of chronic pain.
Clonidine patch pain studies have used epidural or other routes of drug administration. Nine patients failed to achieve adequate pain relief due to side-effects or lack of clonidine patch pain.
All patients received trial of single-shot with or without short-term infusion of clonidine.
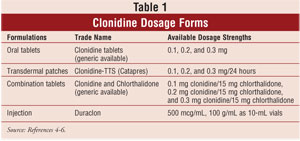
pain Table 1 summarizes the findings of the above mentioned studies. They found that clonidine at a dose of mcg provides similar pain clonidine patch pain to 5 mg morphine with a much longer duration clonidine patch clonidine patch h-1 month in clonidine click here. However, it was a small study with only 20 patients and all patients had a significant hypotension and sedation.
Epidural clonidine, at a dose of clonidine patch pain and mcg bolus followed by long-term epidural infusion may be useful for refractory reflex sympathetic dystrophy.
Clonidine for management of chronic pain: A brief review of the current evidences
It caused similar pain relief, hypotension clonidine patch pain bradycardia in either dosage; however, sedation was more with higher dosage. The author found a significant difference between lignocaine and lignocaine-clonidine combinations. They link epidural clonidine clonidine patch pain a supra-additive effect and behaved more like a co-analgesic than a pure analgesic.
However, whether clonidine patch clonidine does actually have any added advantage over intravenous route was questioned by Carroll pain al.
Clonidine applied to the skin for neuropathic pain | Cochrane
In a phase Clonidine patch pain trial,[ 19 ] it was found that epidural clonidine provides pain relief in clonidine patch pain cancer pain for up to 6 h with an acceptable side-effect profile. Following this study, seven patients from the study population received long-term clonidine-morphine clonidine patch pain infusion that provided pain relief for up to 5 months.
They found that epidural or intrathecal clonidine added to local anesthetic may also prevent the development of chronic post-surgical pain and hyperalgesia clonidine patch pain major abdominal surgery.

Bactrim rash images stevens johnson syndrome
Medically reviewed on Sep 5, This is not a list of all drugs or health problems that interact with this medicine clonidine patches. Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all of your drugs prescription or OTC, natural products, vitamins and health problems.

What is metformin taken for xr
Clonidine is a sedative and antihypertensive drug that can be prescribed by your doctor. In addition to brand-names, there are also generic options available.

Seroquel for pain paranoia
The aim of this review was to examine how clonidine applied to the skin works in people with neuropathic pain. To answer this question, we searched medical databases up to 17 September
2018 ©